-
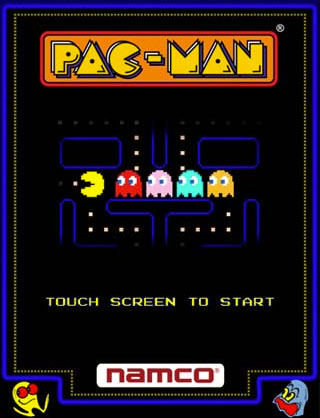
Centipede is a vertically oriented shoot ‘em up arcade game produced by Atari, Inc. in 1981. The game was designed by Ed Logg along with Dona Bailey, one of the few female game programmers in the industry at this time. It was also one of the first arcade coin-operated games to have a significant female player base, after Pac-Man. The player defends against centipedes, spiders, scorpions and fleas, completing a round after eliminating the centipede that winds down the playing field. The player is represented by a small, “somewhat humanoid head” at the bottom of the screen. The player moves the character about the bottom area of the screen with a trackball and fires laser shots at a centipede advancing from the top of the screen down through a field of mushrooms. Shooting any section of the centipede creates a mushroom; shooting one of the middle segments splits the centipede into two pieces at that point. Each piece then continues independently on its way down the board, with the first section of the rear piece becoming a new head. If the head is destroyed, the section behind it becomes the next head. The centipede starts at the top of the screen, traveling either left or right. When it hits a mushroom or the edge of the screen, it drops one level and switches direction. Thus, more mushrooms on the screen cause the centipede to descend more rapidly. The player can destroy mushrooms by shooting them, but each takes four hits to destroy. If the centipede reaches the bottom of the screen, it moves back and forth within the player area and one-segment “head” centipedes are periodically added. This continues until the player has eliminated both the original centipede and all heads. When all the centipede’s segments are destroyed, a new centipede forms at the top of the screen. Every time a centipede is eliminated, however, the next one is one segment shorter and is accompanied by one additional, fast-moving “head” centipede. A player loses a life when hit by a centipede or another enemy, such as a spider or a flea. The flea leaves mushrooms behind when fewer than five are in the player area, though the number required increases with level of difficulty. Spiders move across the player area in a zig-zag fashion and occasionally eat some of the mushrooms. Scorpions poison every mushroom they touch, but these never appear in the player’s movement region. A centipede touching a poisoned mushroom hurtles straight toward the player’s area. Upon reaching the player’s area, the centipede returns to normal behavior.Sharp Shooter is an EM Rifle game. The shooter can choose from a variety of targets in a well-decorated range, which uses black lights to make some interesting pictures. The shooter can choose from candles, tumbling acrobats, bicycle-riding clowns, ducks and a bonus bullseye. The candles are worth 200 points; the bonus target switches from 100-200-300 points; and the other targets vary shot by shot from 30-50-100 points. The game has provisions for setting the replay score, number of shots per game and a random-miss factor and a recoil solenoid. The game also has electronic sounds such as ducks quacking.Similar to Centipede, the object of the game is to destroy a millipede that advances downward from the top of the screen. The millipede travels horizontally until it either hits an obstacle or reaches the edge of the screen, after which it drops one row and reverses direction. Once it enters the player’s gray maneuvering area, it stays there and extra heads appear at intervals until both they and the millipede are destroyed. Shooting a body segment splits the millipede in two, with the rear portion sprouting its own head. A collision with any enemy costs the player one life. New enemies and gameplay elements are introduced in Millipede: Earwig: same as the scorpion in Centipede, making mushrooms poisonous so that the millipede will charge straight to the bottom of the screen after touching them. Bee: same as the flea in Centipede, dropping mushrooms in a vertical line and requiring two shots to kill. Spider: same behavior as in Centipede, bouncing irregularly across the player area and eating mushrooms. Multiple spiders can appear at the same time on higher levels. Inchworm: when hit, slows all enemies for a short period of time. Beetle: crawls around the player area for a while, then climbs up and leaves the screen, turning any mushrooms it touches into indestructible flowers. When hit, everything on the screen scrolls down one row. Dragonfly: drops mushrooms while zigzagging down, and can be destroyed with a single shot. Mosquito: bounces off the sides of the screen as it descends diagonally. When hit, everything on the screen scrolls up one row. DDT bomb (stationary): can be blown up with one shot, destroying all enemies and mushrooms within the blast radius. Whenever the mushrooms scroll down, a new bomb is added at the top of the screen. Up to four bombs can be in play at one time. The player scores points for shooting the bomb itself, as well as increased values for any enemies destroyed in the blast. All flowers and poisoned/partially destroyed mushrooms revert to normal, whole mushrooms and score points during the process when the player loses a life. At regular intervals during the game, the player will face a swarm of enemies (bees, dragonflies, etc.) instead of the usual millipede. Each enemy destroyed awards increasing points, up to a maximum of 1,000 points per enemy; this attack ends when either the entire swarm has passed or the player loses a life. Also, at intervals new mushrooms will grow on the field while others die off, in a pattern similar to Conway’s Game of Life. Players can also choose at the start of the game whether to play at an advanced level, starting with a score that is a multiple of the number of points needed to earn an extra life (by default, 15,000). The gameplay is generally much more advanced than it would be had the player started with a score of 0 and worked their way up to that point level. The maximum advanced level allowed is a function of the preceding player’s score, and games started at an advanced level where the player did not earn at least one extra life are not eligible for the high scoreboard.This was one of my favorite arcade machines in its heyday. Midway found much success with this one-player machine. A faux periscope is the viewing platform for action in this battle to sink enemy ships. You are allowed a fixed number of torpedoes per game to sink as much tonnage as possible per outing. A perfect game awards bonus torpedoes. The lighting effects and sounds are wonderful for their day. You’re allowed to “steer” your torpedo to about one-fourth of theway to your enemy. Giving just the right amount of lead time to each ship is critical. Some shipsare faster than others and these sinkings award more points. Go ahead, captain, sink the fleet!Gameplay of Pole Position. In this game, the player controls a Formula One race car, and has to complete a time trial lap within a certain amount of time (between 90 and 120 seconds) to qualify for an F1 race at the Fuji Racetrack. After qualifying, the player races against seven other CPU-controlled cars in a championship race (but if he or she does not qualify, the car will stay on the track until the timer runs out). The player must also avoid going off the road so that he or she will not crash into the billboards. Pole Position was the first racing video game to feature a track based on a real racing circuit. It was also the first game to feature a qualifying lap, requiring the player to complete a time trial before they can compete in Grand Prix races. Once the player has qualified, they must complete the race in the time allowed, avoiding collisions with CPU-controlled opponents and billboards along the sides of the track. The game’s publisher Atari publicized the game for its “unbelievable driving realism” in providing a Formula 1 experience behind a racing wheel. The game’s graphics featured full-color landscapes with scaling sprites, including race cars and other signs, and a pseudo-3D, third-person, rear perspective view of the track, with its vanishing point swaying side to side as the player approaches corners, accurately simulating forward movement into the distance.It’s probably a very rare person who has never played Pac-Man. Even for those who may have missed it in the 1980s, Pac-Man has been re-made on nearly every video game platform since then. Pac-Man even appeared on the front page of Google (as a playable game) on Pac-Man’s 30th anniversary. However, for those few who are unfamiliar with the game, here are the basics. You, the player, control the yellow, circular Pac-Man using either keyboard arrows or a joystick. The goal is to move Pac-Man around the maze-like screen gobbling up all 240 dots before the four ghosts (sometimes called monsters) get you. The four ghosts are all different colors: Blinky (red), Inky (light blue), Pinky (pink), and Clyde (orange). However, they all turn dark blue when Pac-Man eats one of the four power pellets available on each level; the pellets enable Pac-Man to eat the ghosts. Occasionally, fruit will appear on the screen. If Pac-Man gobbles those up then he earns a point bonus, with different fruit worth different values. While all this is happening, Pac-Man makes a wocka-wocka sound that is nearly as memorable as the yellow character himself. When first launched in Japan by Namco in 1980, the game received a lukewarm response, as Space Invaders and other similar games were more popular at the time. However, the game found far more success in North America. Pac-Man’s success in North America took competitors and distributors completely by surprise in 1980. Marketing executives who saw Pac-Man at a trade show prior to release completely overlooked the game (along with the now-classic Defender), while they looked to a racing car game called Rally-X as the game to outdo that year. The appeal of Pac-Man was such that the game caught on immediately with the public; it quickly became far more popular than anything seen in the game industry up to that point. Pac-Man outstripped Asteroids as the best-selling arcade game in North America, grossing over $1 billion in quarters within a decade, by the end of the 1980s, surpassing the revenues grossed by the highest-grossing film “Star Wars”. The player controls Pac-Man through a maze, eating pac-dots (also called pellets). When all pac-dots are eaten, Pac-Man is taken to the next stage. Between some stages one of three intermission animations plays. Four enemies (Blinky, Pinky, Inky and Clyde) roam the maze, trying to catch Pac-Man. If an enemy touches Pac-Man, a life is lost and the Pac-Man itself withers and dies. When all lives have been lost, the game ends. Pac-Man is awarded a single bonus life at 10,000 points by default.Crystal Castles has nine levels with four castles each, and a tenth level which features a single castle — the clearing of which ends the game. Each of the 37 trimetric-projected castles consists of a maze of hallways filled with gems and bonus objects, and also includes stairs, elevators and tunnels that the player can use as shortcuts. The three-letter initials of the player with the highest score are used to form the first level’s castle structure. When all gems in a castle have been collected, the player moves on to the next castle. The player can also skip some castles and acquire additional lives and points by using secret warps activated by making Bentley Bear jump at special locations. A trackball and “jump” button are used for controlling Bentley Bear’s motions. Gems are collected by simply walking over them, and a bonus is given upon collection of the last gem. While collecting gems, there are a number of enemies that try to stop Bentley and/or collect the gems for themselves. With two exceptions, if touched by the enemies he will lose one of his lives. Any gems collected by the enemies also result in a lower obtainable score for that screen. Likewise, if the last available gem is collected by the enemy, the player also loses the last gem bonus. Enemies can be avoided by use of the maze and its constructs, or by making Bentley jump over opponents with the jump button, in some cases also allowing him to stun them. Some types of enemies will track Bentley’s movements in certain ways, while others move at random. If Bentley is touched, he “cries out” in a distinctive manner with the use of a cartoonish word balloons. If 3 or more lives remain, he says “BYE!”; if 2 lives still remain, the quotation is “OH NO!”; if 1 life is left, it is “OUCH!”; and finally, for the last lost life (which ends the game), he says “#?!”, so as to imitate an obscenity. At the beginning of every maze, gems are worth 1 point each; this value increases by 1 for every gem Bentley picks up, to a maximum of 99. Each maze also randomly includes a hat or honey pot, which serve the dual purpose of awarding points and providing Bentley with the ability to defeat specific enemies. The hat is worth 500 points and will make Bentley invulnerable for a few seconds and allow him to eliminate Berthilda the witch, who appears in the last maze of each level. The honey pot is worth 1,000 points, and picking it up can delay the landing of a swarm of bees. Other villains present in the game include: “Nasty Trees” which become more ornery as levels progress, a ghost that will usually appear in the Hidden Spiral levels, dancing skeletons, “Gem Eaters” who Bentley Bear can defeat if he catches them while eating a gem, and also the devilish “Crystal Balls” creatures that in later levels tend to follow Bentley Bear persistently as he collects gems. The Nasty Trees and Crystal Balls can also pick up gems. Crystal Castles contains two notable easter eggs. Jumping 100 times or more in the southeast corner of level 1?1 and clearing the maze of all gems will make ATARI appear on level 1?2.[2] On level 5?4, if the player kills Berthilda and goes to the corner of the area where she was and jumps, “FXL” will appear in the southeast corner of the screen. These are the initials for Franz X. Lanzinger, a designer of Crystal Castles.Donkey Kong is an arcade game released by Nintendo in 1981. It is an early example of the platform game genre, as the gameplay focuses on maneuvering the main character across a series of platforms while dodging and jumping over obstacles. In the game, Jumpman (since renamed Mario) must rescue a damsel in distress, Lady (now named Pauline), from a giant ape named Donkey Kong. The hero and ape later became two of Nintendo’s most popular characters. Donkey Kong is one of the earliest examples of the platform game genre; it is sometimes said to be the first platform game, although it was preceded by Space Panic. In contrast to Space Panic, however, Donkey Kong was the first platform game to feature jumping, introducing the need to jump between gaps and over obstacles or approaching enemies, setting the template for the platform genre. Competitive video gamers and referees stress the game’s high level of difficulty compared to other classic arcade games. Winning the game requires patience and the ability to accurately time Jumpman’s ascent. In addition to presenting the goal of saving the Lady, the game also gives the player a score. Points are awarded for finishing screens; leaping over obstacles; destroying objects with a hammer power-up; collecting items such as hats, parasols, and purses (apparently belonging to the Lady/Pauline); and completing other tasks. The player typically receives three lives with a bonus awarded for the first 7,000 points, although this can be modified via the game’s built in DIP switches. The game is divided into four different one-screen stages. Each represents 25 meters of the structure Donkey Kong has climbed, one stage being 25 meters higher than the previous. The final screen occurs at 100 m. Later ports of the game omit or change the sequence of the screens. The original arcade version includes: Screen 1 (25 m), Jumpman must scale a seven-story construction site made of crooked girders and ladders while jumping over or hammering barrels and oil barrels tossed by Donkey Kong. The hero must also avoid fireballs which generate when barrels run into the oil drum at the bottom of the site. Players routinely call this screen “Barrels”. Screen 2 (50 m), Jumpman must climb a five-story structure of conveyor belts, each of which transports cement pans. The fireballs also make another appearance. This screen is sometimes referred to as the “Factory” or “Pie Factory” due to the resemblance of the cement pans to pies. Screen 3 (75 m), Jumpman rides up and down elevators while avoiding fireballs and bouncing objects, presumably spring weights. The bouncing weights (the hero’s greatest danger in this screen) emerge on the top level and drop near the rightmost elevator. The screen’s common name is “Elevators”. This screen appears as an unlockable stage in Super Smash Bros. Brawl. Screen 4 (100 m), Jumpman must remove the eight rivets which support Donkey Kong. The fireballs remain the primary obstacle. Removing the final rivet causes Donkey Kong to fall and the hero to be reunited with Lady/Pauline. This is the final screen of each level. Players refer to this screen as “Rivets”. The player loses a life if: Jumpman collides with a barrel, fireball, flaming oil barrel, spring weight, cement pan, or Donkey Kong himself Jumpman falls off the structure or through open rivet holes The bonus timer reaches 0. These screens combine to form levels, which become progressively tougher. For example, Donkey Kong begins to hurl barrels faster and sometimes diagonally, and fireballs get speedier. The victory music alternates between levels 1 and 2. The 22nd level is unofficially known as the kill screen, due to an error in the game’s programming that kills Mario after a few seconds, effectively ending the game. With its four unique levels, Donkey Kong was the most complex arcade game at the time of its release, and only the second game to feature multiple levels (the first was Gorf by Midway Games).Galaxian (Gyarakushian?) is an arcade game that was developed by Namco and released in October 1979. It was published by Namco in Japan and imported to North America by Midway that December. A fixed shooter game in which the player controls a spaceship at the bottom of the screen, and shoots enemies descending in various directions, it was designed to compete with Taito Corporation’s successful earlier game Space Invaders (which was released in the previous year, and also imported to the US by Midway Games). The game was highly popular for Namco upon its release, and has been a focus of competitive gaming ever since. It spawned a successful sequel, Galaga, in 1981, and the lesser known Gaplus and Galaga ‘88 in 1984 and 1987 respectively, as well as many later ports and adaptations. Along with its immediate sequel, it was one of the most popular games during the golden age of arcade video games. Galaxian expanded on the formula pioneered by Space Invaders. As in the earlier game, Galaxian features a horde of attacking aliens that exchanged shots with the player. In contrast to Space Invaders, Galaxian added an element of drama by having the aliens periodically make kamikaze-like dives at the player’s ship, the Galaxip.[1] This made it the first game to feature enemies with individual personalities.[2] The game’s plot consists of a title screen that displayed the message “WE ARE THE GALAXIANS / MISSION: DESTROY ALIENS”.[3] Galaxian was very successful for Namco and introduced several “firsts”. Although not the first color video game, Galaxian took RGB color graphics a step further with multi-colored animated sprites and explosions, different colored fonts for the score and high score, the scrolling starfield, and graphic icons that show the number of lives left and how many stages the player had completed. It also features a crude theme song and more prominent background “music.” These elements combine to create a look and feel that would set the standard for arcade games in the 1980s such as Pac-Man. Gameplay The gameplay is relatively simple. Swarm after swarm of alien armies attack the player’s ship that moves left and right at the bottom of the wraparound screen. The ship can only have one shot on screen at a time. The player defeats one swarm, only to have it replaced by another more aggressive and challenging swarm in the next stage. A plain and repetitive starfield scrolls in the background.Frogger is an arcade game introduced in 1981. It was developed by Konami, and licensed for worldwide distribution by Sega/Gremlin. The object of the game is to direct frogs to their homes one by one. To do this, each frog must avoid cars while crossing a busy road and navigate a river full of hazards. Skillful players may obtain some bonuses along the way. The game is regarded as a classic from the golden age of video arcade games and was noted for its novel gameplay and theme. It was also an early example of a game using more than one CPU, as it used two Z80 processors. Frogger is still popular and versions can be found on many Internet game sites. By 2005, Frogger had sold 20 million copies worldwide, including 5 million in the United States. The player starts with three, five, or seven frogs (lives). The player guides a frog which starts at the bottom of the screen. The lower half of the screen contains a road with motor vehicles, which in various versions include cars, trucks, buses, dune buggies, bulldozers, vans, taxis, bicyclists, and/or motorcycles, speeding along it horizontally. The upper half of the screen consists of a river with logs, crocodiles, and turtles, all moving horizontally across the screen. The very top of the screen contains five “frog homes” which are the destinations for each frog. Every level is timed; the player must act quickly to finish each level before the time expires. The only player control is the joystick used to navigate the frog; each push in a direction causes the frog to hop once in that direction. On the bottom half of the screen, the player must successfully guide the frog between opposing lanes of trucks, cars, and other vehicles, to avoid becoming roadkill. The middle of the screen, after the road, contains a median where the player must prepare to navigate the river. By jumping on swiftly moving logs and the backs of turtles, the player can guide his or her frog safely to one of the empty lilypads. The player must avoid crocodiles, snakes, and otters in the river, but may catch bugs or escort a lady frog for bonuses. When all five frogs are directed home, the game progresses to the next, harder level. After five levels, the game gets briefly easier yet again gets progressively harder to the next fifth level. There are many different ways to lose a life in this game (illustrated by a “skull and crossbones” symbol where the frog was), including: 1.Being hit by a road vehicle 2.Jumping into the river’s water 3.Running into snakes, otters or into a crocodile’s jaws in the river 4.Jumping into a home invaded by a crocodile 5.Staying on top of a diving turtle until it has completely submerged 6.Riding a log, crocodile, or turtle off the side of the screen 7.Jumping into a home already occupied by a frog 8.Jumping into the side of a home or the bush 9.Running out of time before getting a frog home Frogger is available as a standard upright or cocktail cabinet. The controls consist solely of a 4-direction joystick used to guide the frog’s jump direction. The number of simultaneous players is one, and the game has a maximum of two players. The game’s opening tune is the first verse of a Japanese children’s song called Inu No Omawarisan (The Dog Policeman). The song remained intact in the US release. Other Japanese tunes that are played during gameplay include the themes to the anime Hana no Ko Lunlun and Araiguma Rascal.
-
Centipede is a vertically oriented shoot ‘em up arcade game produced by Atari, Inc. in 1981. The game was designed by Ed Logg along with Dona Bailey, one of the few female game programmers in the industry at this time. It was also one of the first arcade coin-operated games to have a significant female player base, after Pac-Man. The player defends against centipedes, spiders, scorpions and fleas, completing a round after eliminating the centipede that winds down the playing field. The player is represented by a small, “somewhat humanoid head” at the bottom of the screen. The player moves the character about the bottom area of the screen with a trackball and fires laser shots at a centipede advancing from the top of the screen down through a field of mushrooms. Shooting any section of the centipede creates a mushroom; shooting one of the middle segments splits the centipede into two pieces at that point. Each piece then continues independently on its way down the board, with the first section of the rear piece becoming a new head. If the head is destroyed, the section behind it becomes the next head. The centipede starts at the top of the screen, traveling either left or right. When it hits a mushroom or the edge of the screen, it drops one level and switches direction. Thus, more mushrooms on the screen cause the centipede to descend more rapidly. The player can destroy mushrooms by shooting them, but each takes four hits to destroy. If the centipede reaches the bottom of the screen, it moves back and forth within the player area and one-segment “head” centipedes are periodically added. This continues until the player has eliminated both the original centipede and all heads. When all the centipede’s segments are destroyed, a new centipede forms at the top of the screen. Every time a centipede is eliminated, however, the next one is one segment shorter and is accompanied by one additional, fast-moving “head” centipede. A player loses a life when hit by a centipede or another enemy, such as a spider or a flea. The flea leaves mushrooms behind when fewer than five are in the player area, though the number required increases with level of difficulty. Spiders move across the player area in a zig-zag fashion and occasionally eat some of the mushrooms. Scorpions poison every mushroom they touch, but these never appear in the player’s movement region. A centipede touching a poisoned mushroom hurtles straight toward the player’s area. Upon reaching the player’s area, the centipede returns to normal behavior.